Transient receptor potential cation channel 6 contributes to kidney injury induced by diabetes and hypertension | American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology

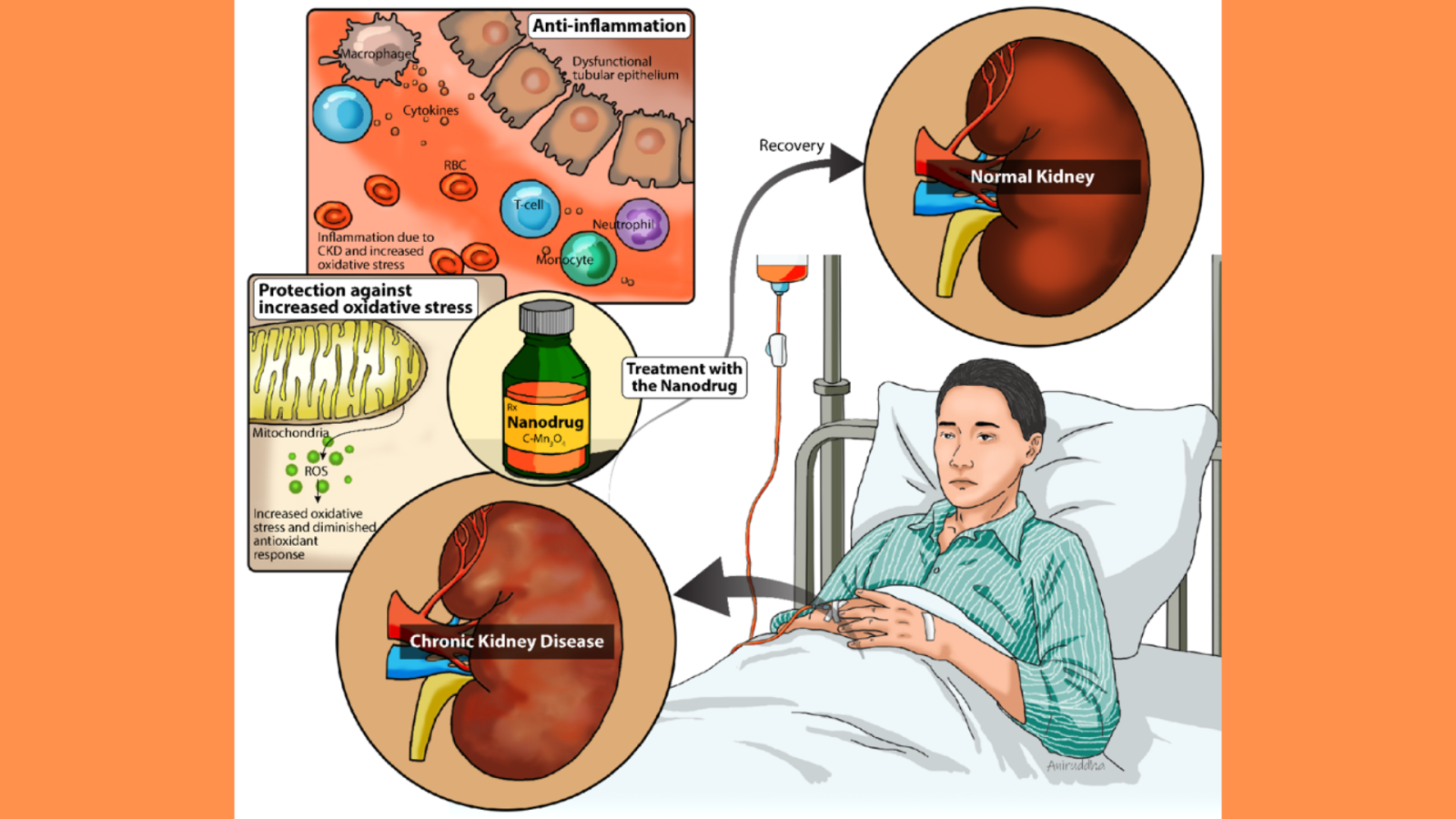
Renal Cell-Targeted Drug Delivery Strategy for Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Mini-Review | Molecular Pharmaceutics
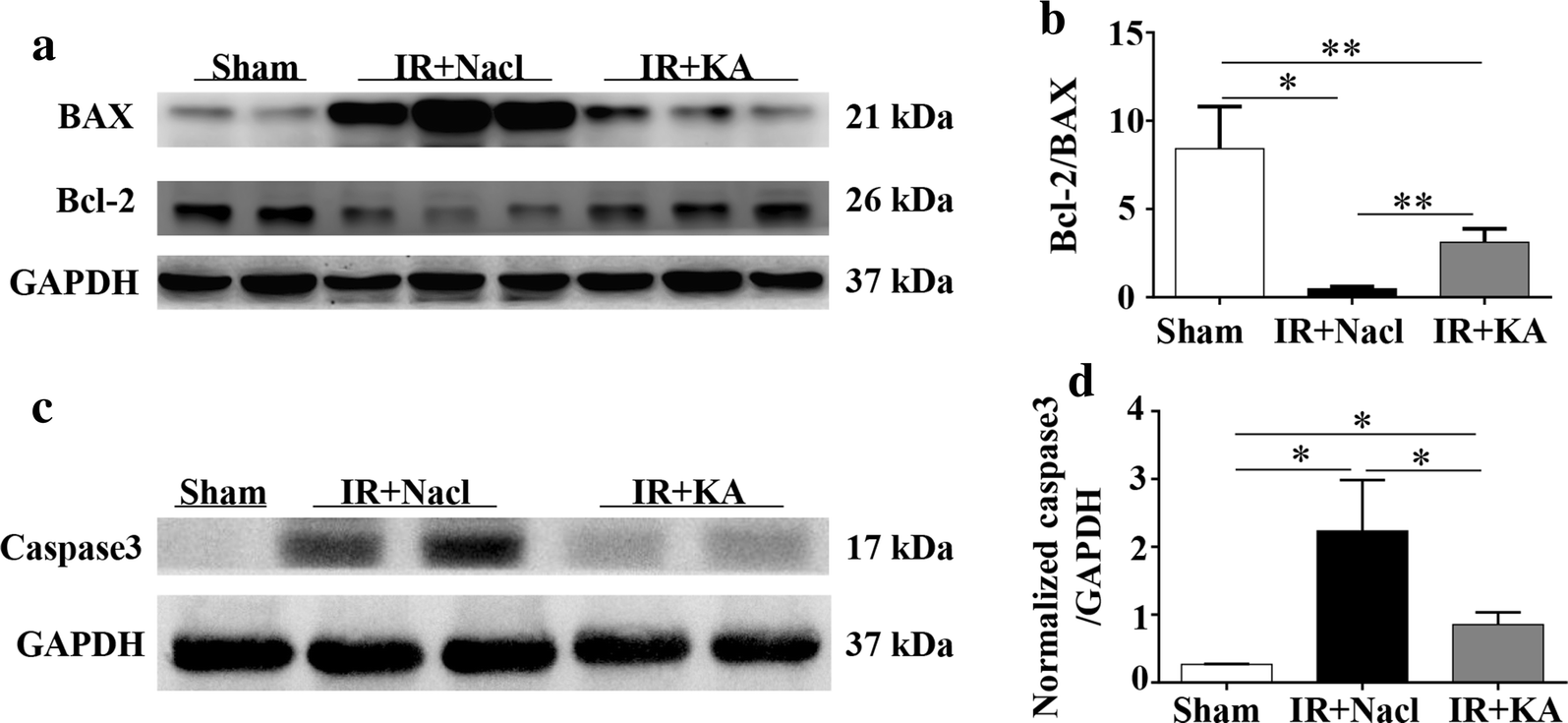
Compound α-keto acid tablet supplementation alleviates chronic kidney disease progression via inhibition of the NF-kB and MAPK pathways | Journal of Translational Medicine | Full Text

Endoplasmic reticulum stress is activated in post-ischemic kidneys to promote chronic kidney disease - eBioMedicine
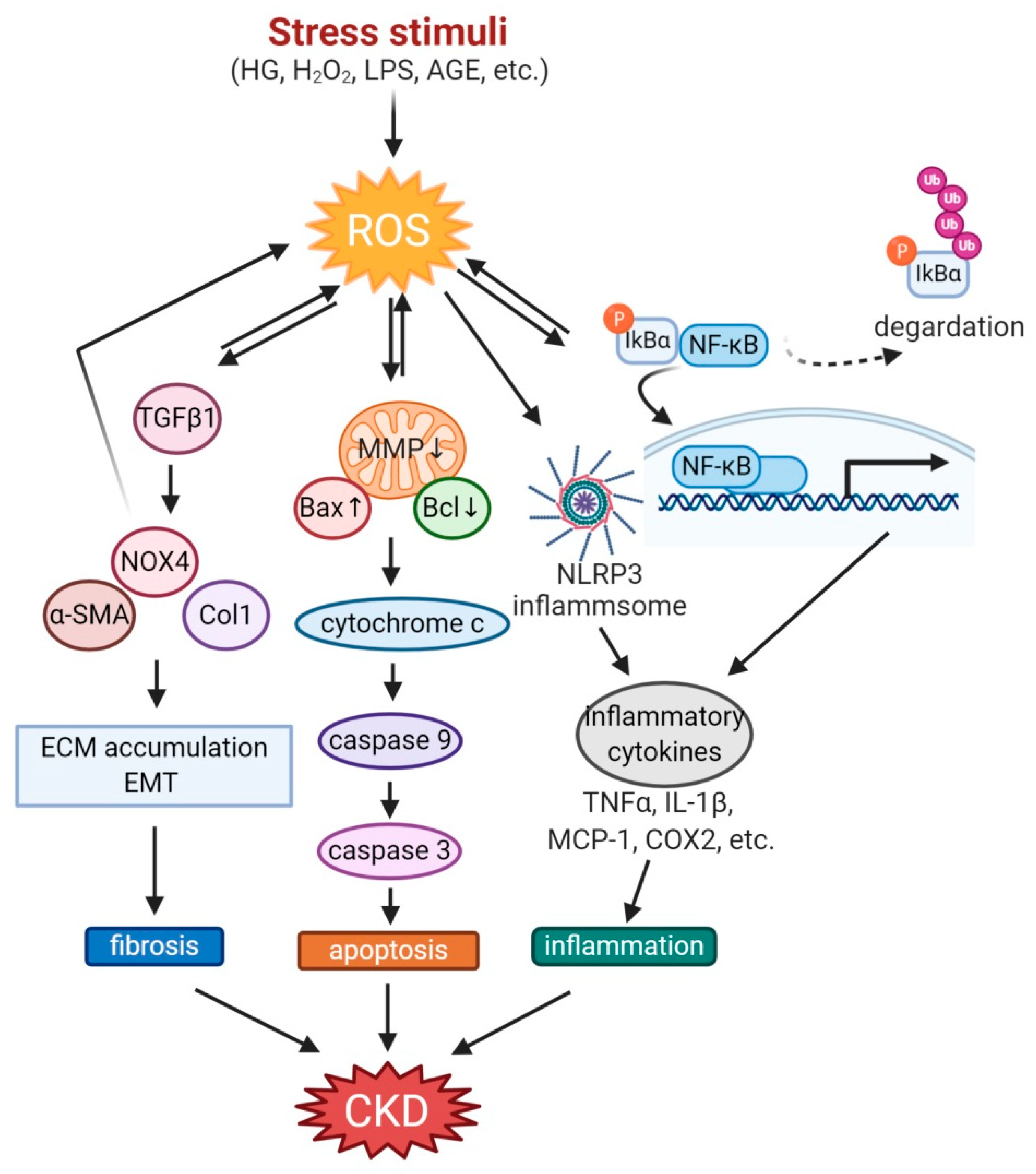
Antioxidants | Free Full-Text | Pharmacotherapy against Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease: Promising Small Molecule Natural Products Targeting Nrf2-HO-1 Signaling

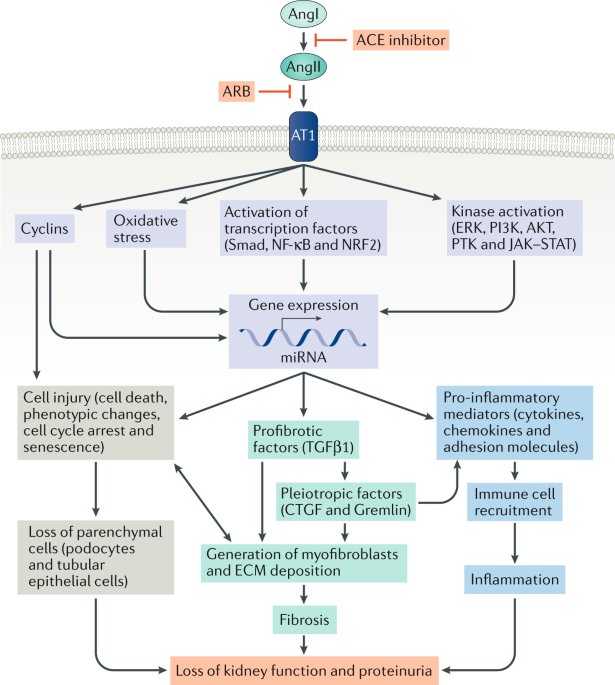
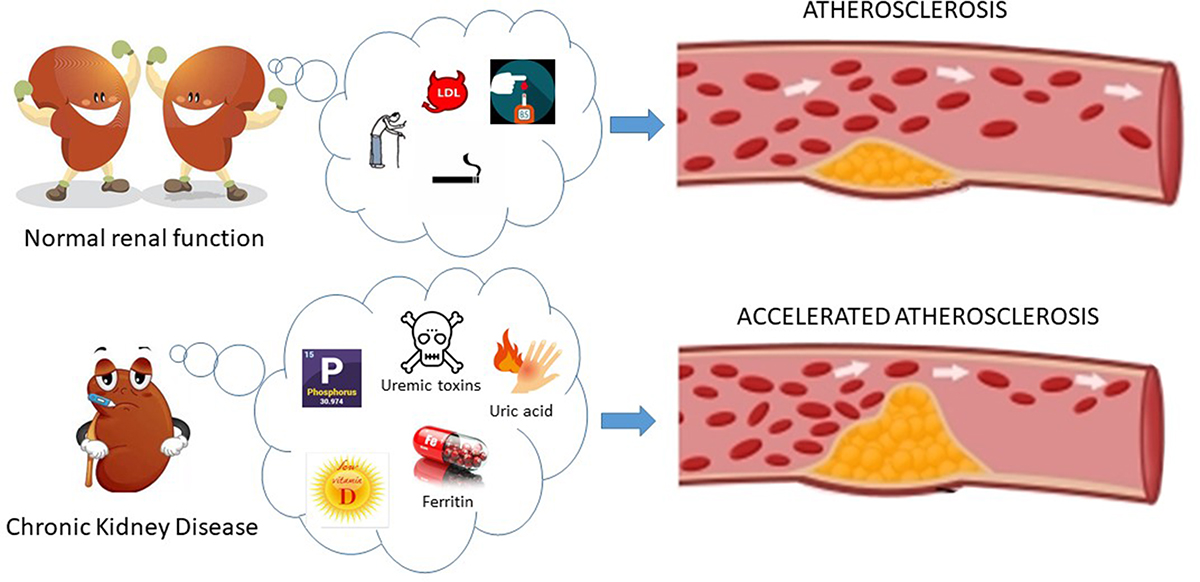
Interrelationship Between Cardiac Hypertrophy, Heart Failure, and Chronic Kidney Disease | Circulation Research

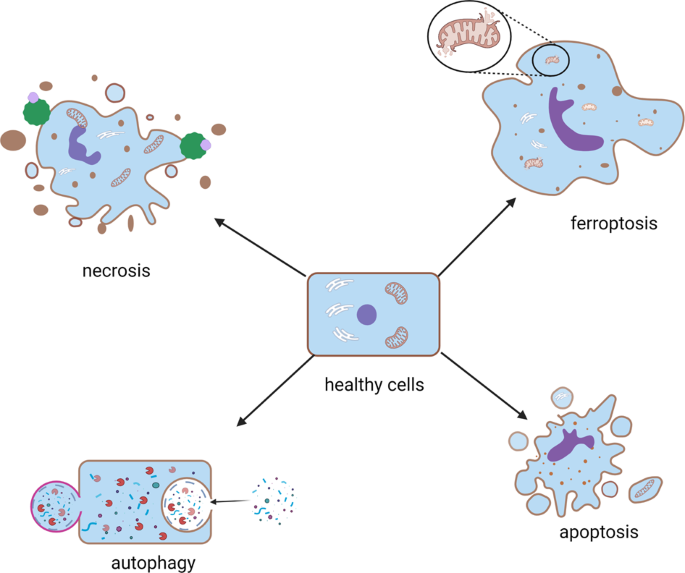
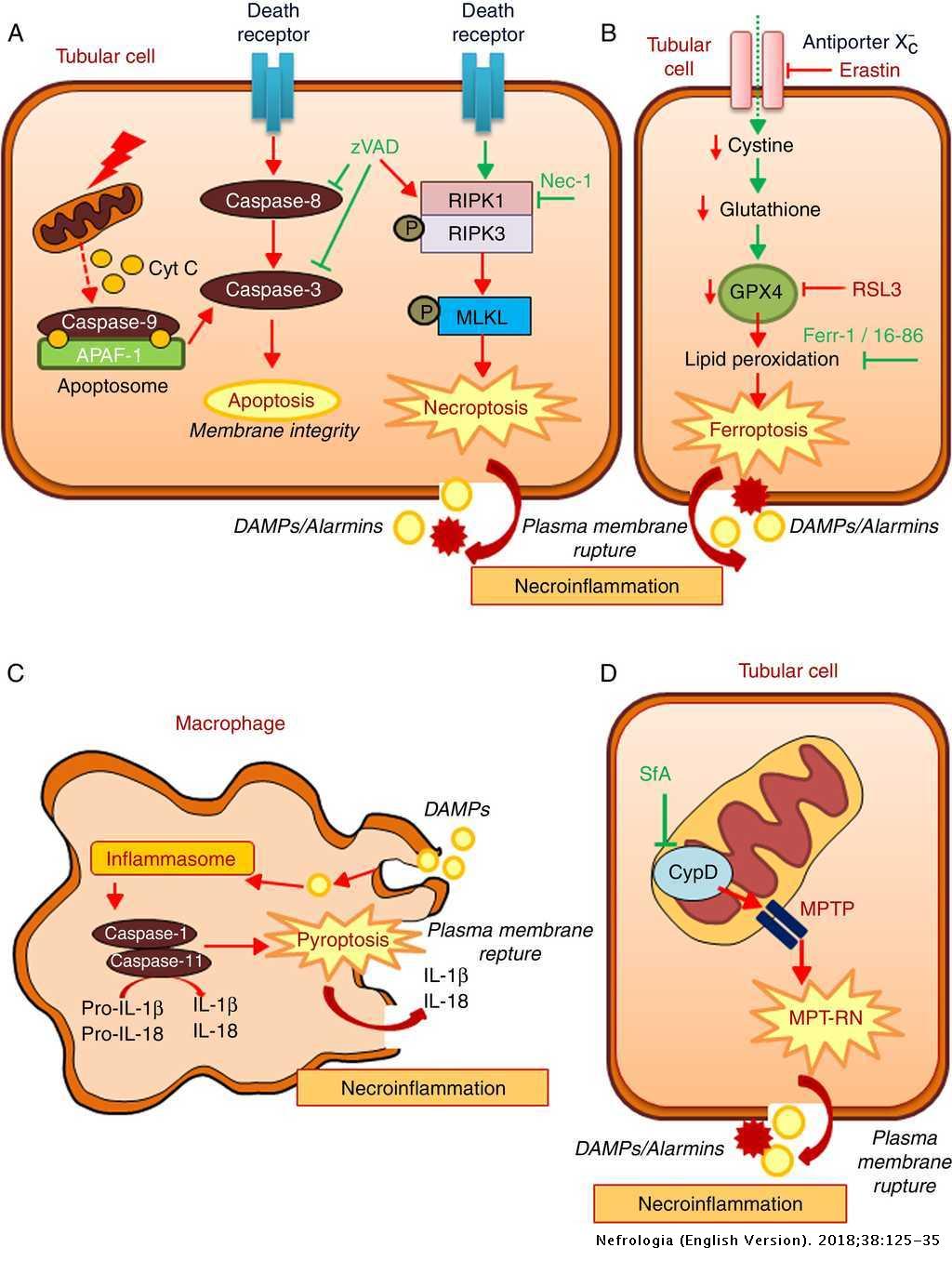
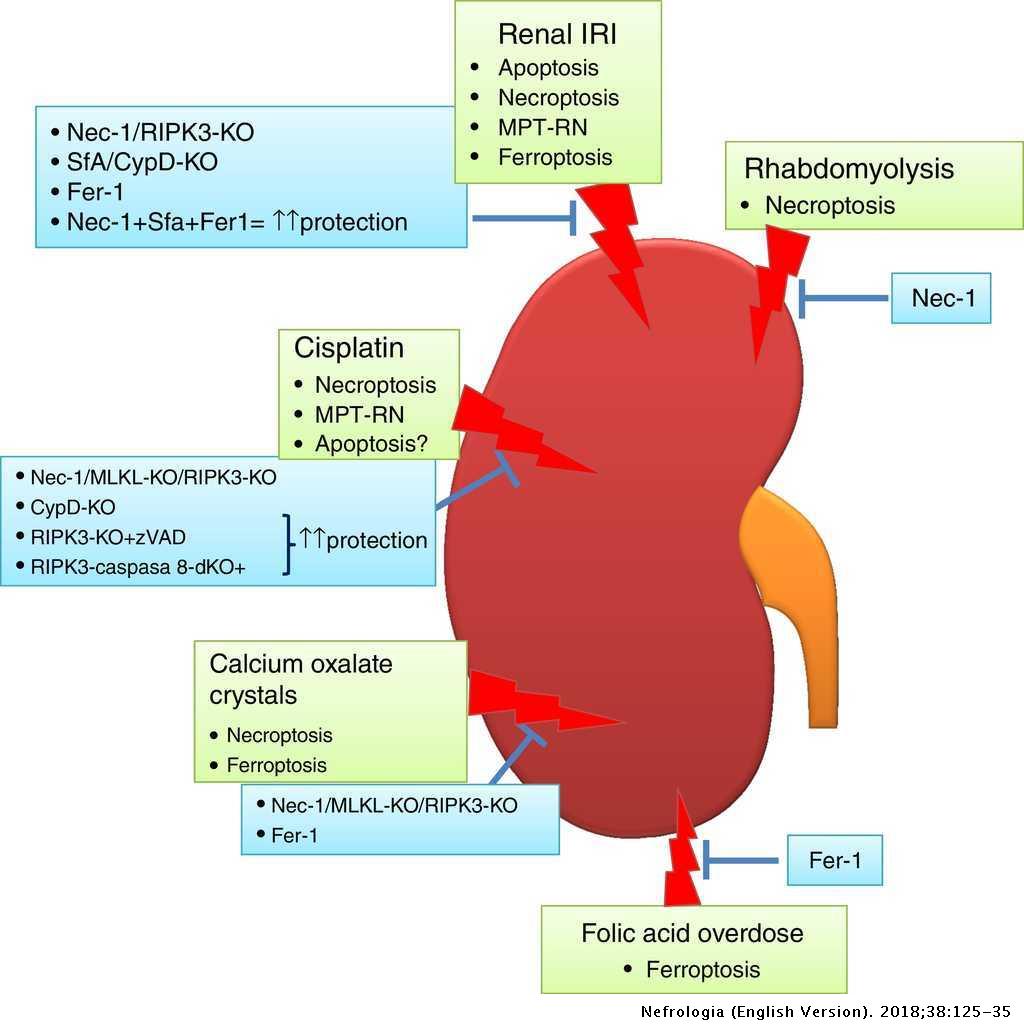
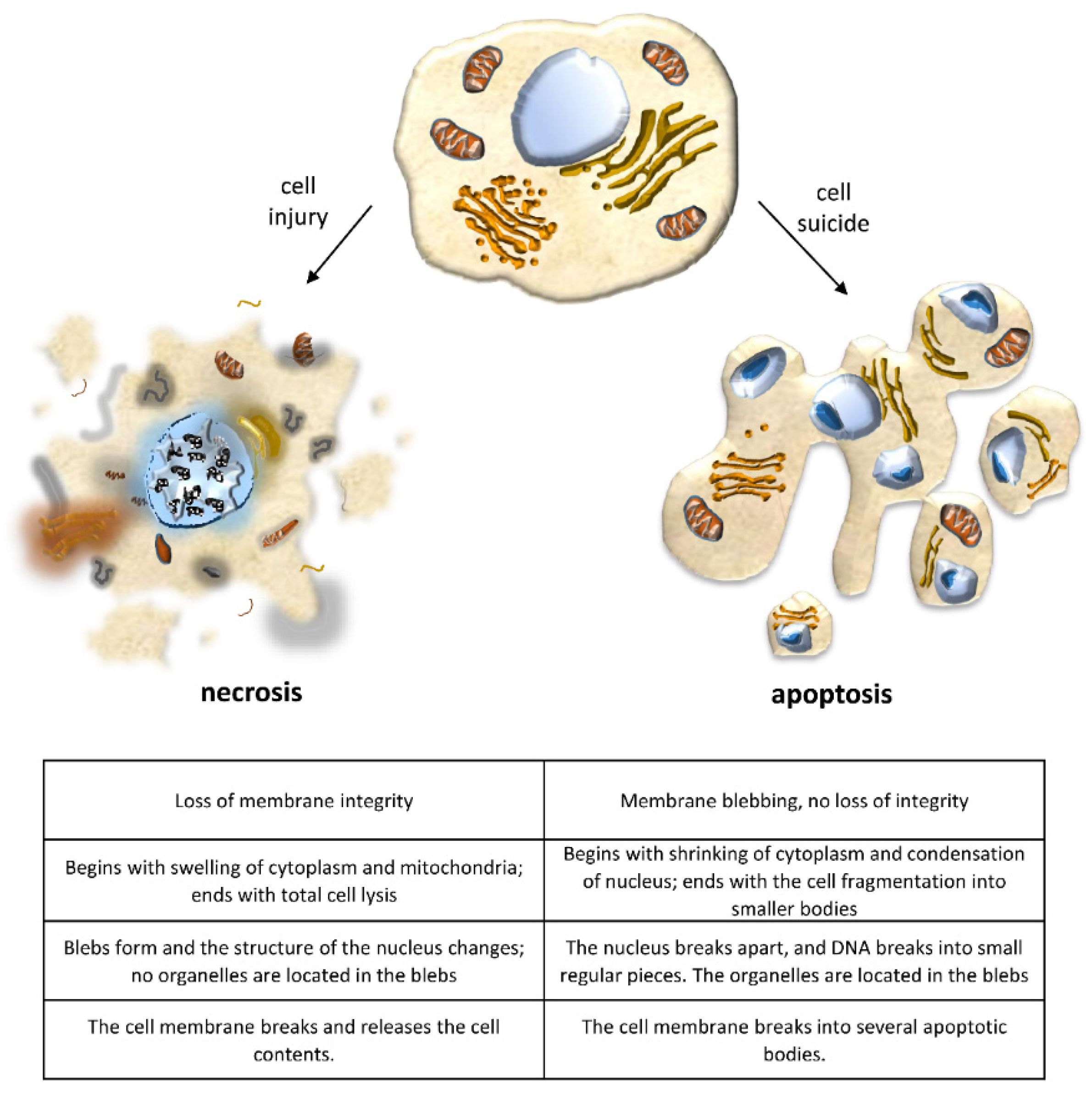
Regulated necrosis and failed repair in cisplatin-induced chronic kidney disease - Kidney International

An Activatable Near-Infrared Fluorescence Probe for in Vivo Imaging of Acute Kidney Injury by Targeting Phosphatidylserine and Caspase-3 | Journal of the American Chemical Society

Lactobacillus rhamnosus GKLC1 ameliorates cisplatin-induced chronic nephrotoxicity by inhibiting cell inflammation and apoptosis - ScienceDirect

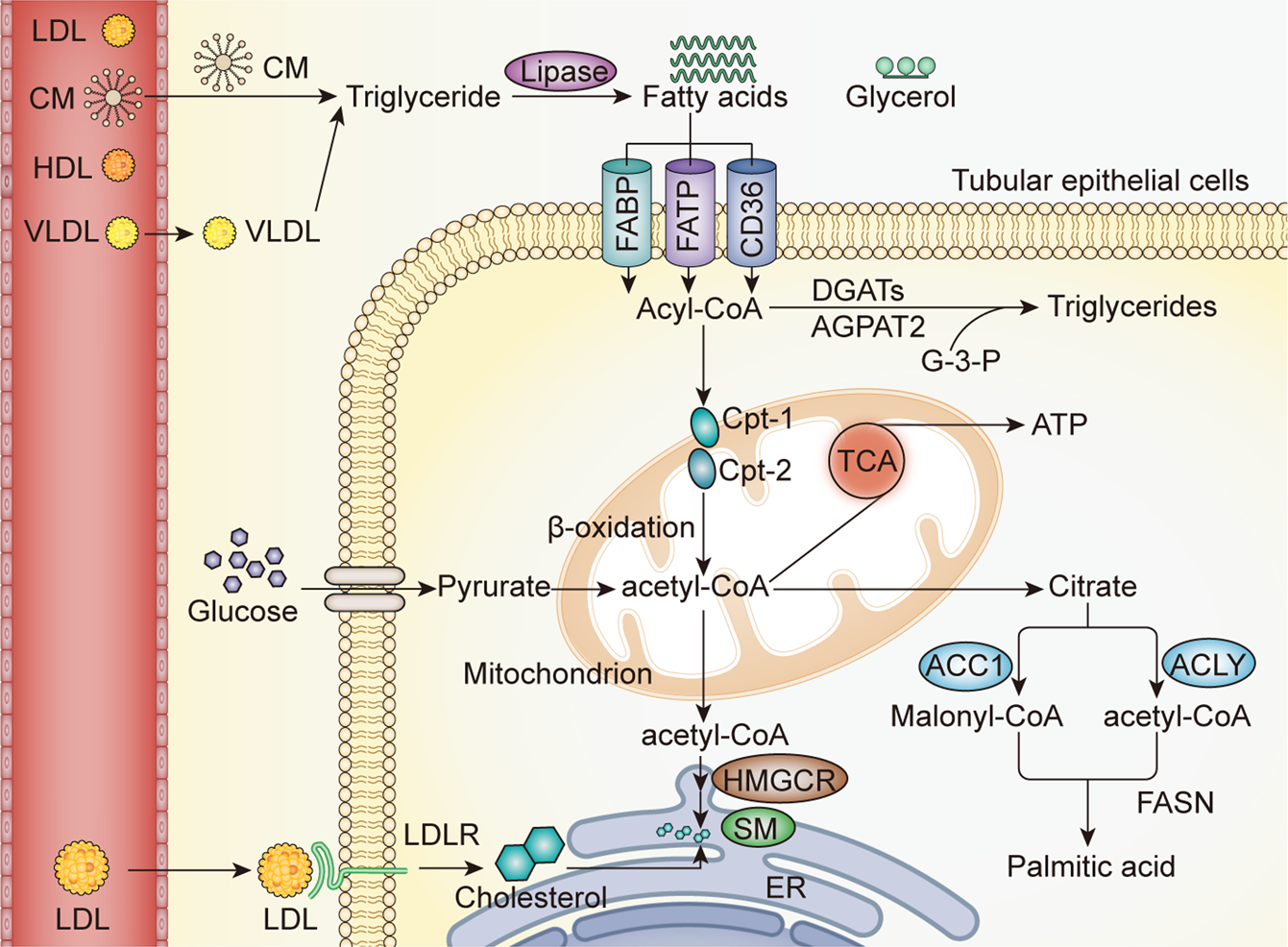
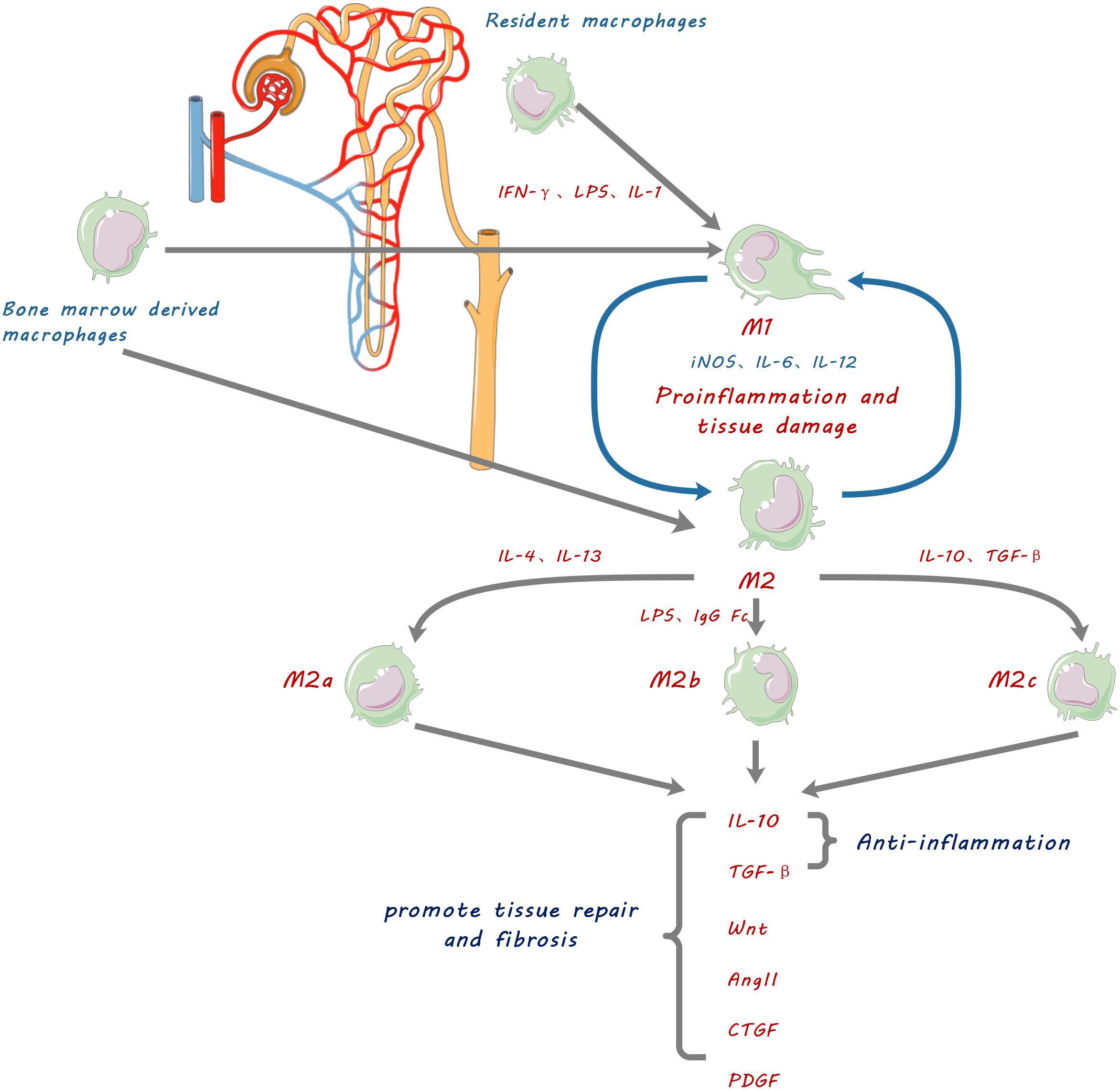
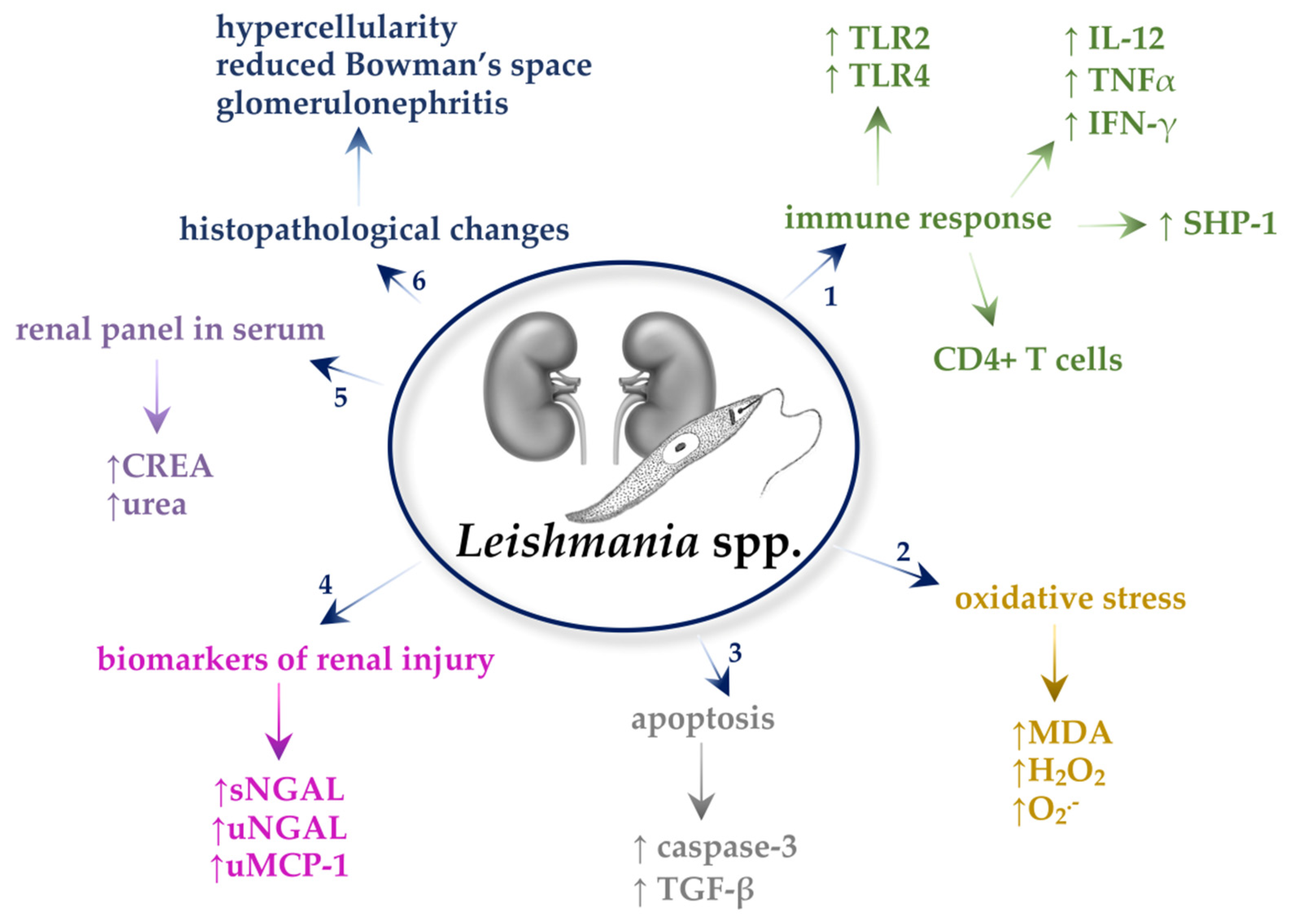
Frontiers | Current Challenges and Future Perspectives of Renal Tubular Dysfunction in Diabetic Kidney Disease